1 1 Vectors Representation Of A Vector Prob 1

1 1 Vectors Representation Of A Vector Prob 1 Youtube 1.1 introduction to vectors. 1.1. introduction to vectors. vectors as objects which have both length and direction arise in physics and geometry to describe quantities such as forces and velocities. as lists of numbers, they also appear in areas such as data science. in the first chapter of this course, we will consider vectors as elements of. Chapter 1: introduction to vectors1.1. vectors and linear combina. ionslet's begin by saying what vectors are: they are lists of numbers. if there are 2 numbers in the list, there is a natural. correspondence to a point in a plane, determined by the choice of axes. if there are. numbers in the list, it corresponds to a point in 3 dimensional.
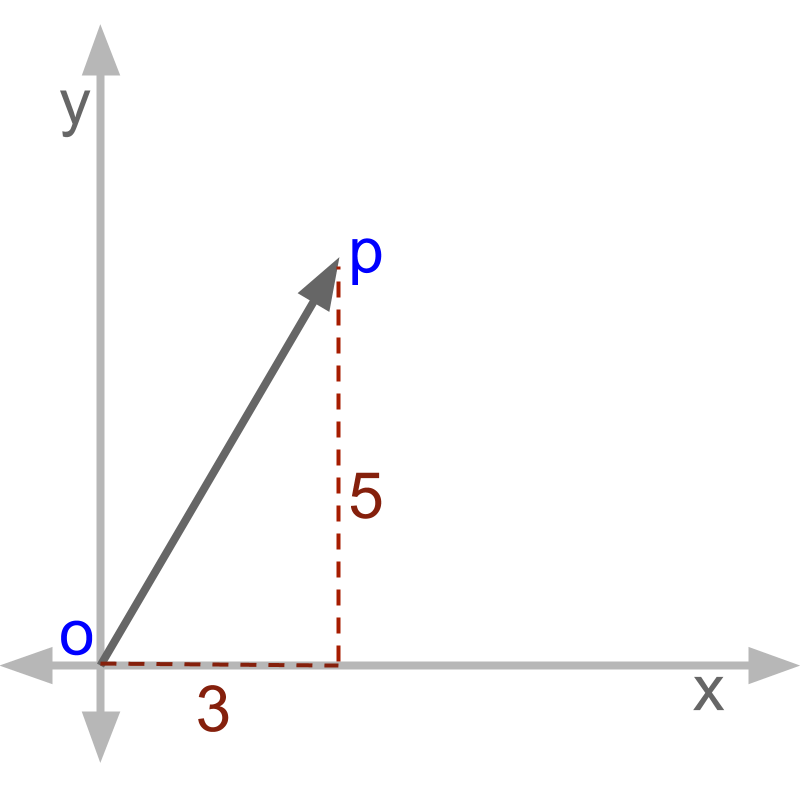
Vector Algebra Mathematical Representation Of Vectors These concepts apply to any vector space. a linear combination of vectors~a and~b is an expression of the form ~a ~b. this linear combination yields another vector ~v. the set of all such vectors, obtained by taking any ; 2r, is itself a vector space (or more correctly a vector ‘subspace’ if ~a and ~b are two vectors in e3 for instance). Since the starting and ending points of the given vector are p and q respectively, the vector is − − → p q p q →. answer: − − → p q p q →. example 2: find the components of vector − − → p q p q → that is mentioned in example 1. solution: the given position vectors are: − − → op o p → = < 5, 4, 3>. Chapter 1. introduction to vectors and vector functions section 1.1 vectors. definition. a two dimensional vector is an ordered paira =< a1, a2 > of real numbers. the numbers a1 and a2 are called the components ofa . −→. a representation of the vectora =< a1, a2 > is a directed line segment ab from any point a(x, y) to the point b(x a1, y. Therefore we can write a vector as a simple product: →a = aˆa. where ˆa is the unit vector (usually pronounced “ a hat”). it is a unitless vector of length 1 that points in the direction of the vector →a. the value a is a number with physical units that equals the magnitude.
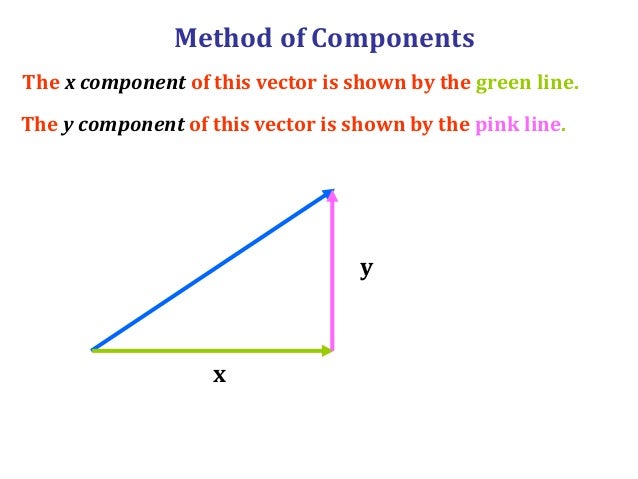
1 1 Vectors Chapter 1. introduction to vectors and vector functions section 1.1 vectors. definition. a two dimensional vector is an ordered paira =< a1, a2 > of real numbers. the numbers a1 and a2 are called the components ofa . −→. a representation of the vectora =< a1, a2 > is a directed line segment ab from any point a(x, y) to the point b(x a1, y. Therefore we can write a vector as a simple product: →a = aˆa. where ˆa is the unit vector (usually pronounced “ a hat”). it is a unitless vector of length 1 that points in the direction of the vector →a. the value a is a number with physical units that equals the magnitude. Directed line segments and vectors. a directed line segment is defined as an initial point, , and a terminal point . definition: vector. a vector is the equivalence class of all directed segments of the same length and direction. we can represent a vector by writing the unique directed line segment that has its initial point at the origin. Properties of vectors. a two dimensional vector is represented graphically as an arrow with a tail and a head. the head is the arrow and is also called the terminal point. when finding the vector between two points start with the terminal point and subtract the initial point (the tail).

Comments are closed.