1 1 Real Numbers Algebra Essentials Part 1 Classifying Real Numbers

1 1 Real Numbers Algebra Essentials Part 1 Classifying Real Numbers The property states that, for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2 because. Exercise 1.1.7. learning objectives. classify a real number as a natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational number. perform calculations using order of operations. use the following properties of real numbers: commutative, associative, distributive, inverse, and identity. evaluate algebraic expressions.

Lesson 1 1 A Basic 1 Real Numbers Algebra Essentials Part 1 The property states that for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2. because. Examples: • 1 2 is a rational number. • 0.75 is a rational number (3 4) • 1 is a rational number (1 1) • 2 is a rational number (2 1) • 2.12 is a rational number (212 100) • −6.6 is a rational number (−66 10) irrational numbers real numbers that cannot be written as a simple fraction. 1.5 is rational, but π is irrational. 1.1 real numbers: algebra essentials. topics covered in this section are: classify a real number as a natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational number. perform calculations using order of operations. use the following properties of real numbers: commutative, associative, distributive, inverse, and identity. evaluate algebraic expressions. The property states that, for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2 because.
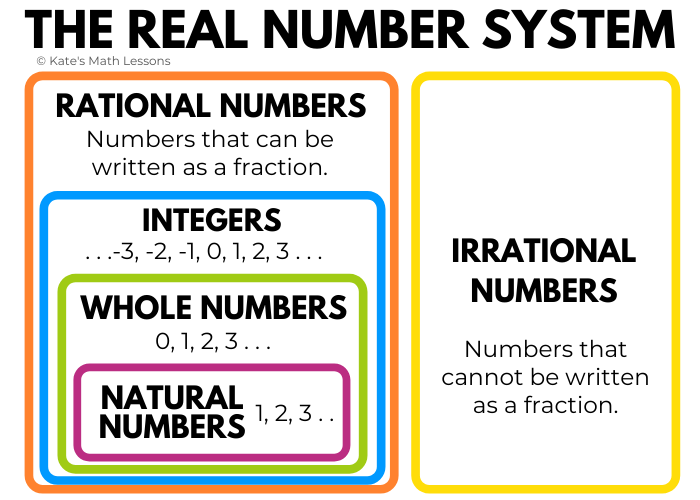
Classifying Real Numbers Kate S Math Lessons 1.1 real numbers: algebra essentials. topics covered in this section are: classify a real number as a natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational number. perform calculations using order of operations. use the following properties of real numbers: commutative, associative, distributive, inverse, and identity. evaluate algebraic expressions. The property states that, for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2 because. Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: classify a real number as a natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational number. perform calculations using order of operations. use the following properties of real numbers: commutative, associative, distributive, inverse, and identity. evaluate algebraic expressions. This is an irrational number because when written in decimal form, it is non terminating and non repeating. this is also a real number. first, we need to simplify this radical expression which gives us 6 = – \sqrt {16} = – \,4 16. the number – \,4 is an integer, a rational number, and a real number.

Chapter 1 Pdf 1 1 Real Numbers Algebra Essentials Classifying A Real Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: classify a real number as a natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational number. perform calculations using order of operations. use the following properties of real numbers: commutative, associative, distributive, inverse, and identity. evaluate algebraic expressions. This is an irrational number because when written in decimal form, it is non terminating and non repeating. this is also a real number. first, we need to simplify this radical expression which gives us 6 = – \sqrt {16} = – \,4 16. the number – \,4 is an integer, a rational number, and a real number.

College Algebra Section 1 1 Real Numbers Youtube

Comments are closed.