🥇 Pelvic Diaphragm Pelvic Floor Muscles

Muscles Of True Pelvis And Pelvic Diaphragm Anatomy Qa 1 4. synonyms: pubovisceral muscle, musculus pubovisceralis. the pelvic floor is primarily made up of thick skeletal muscles along with nearby ligaments and their investing fascia. it is a basin shaped muscular diaphragm that helps to support the visceral contents of the pelvis. the main focus of this article will be the pelvic floor muscles. Diaphragm: contracts and flattens pushing your organs downward and increasing pressures in your abdominal cavity and on your pelvic floor. pelvic floor: the muscles lengthen and relax to accommodate the increased pressures above. at the same time, your ribs expand to make room for the descending abdominal organs. exhale:.

3 The Pelvic Floor Simplemed Learning Medicine Simplified The pelvic floor is a funnel shaped structure. it attaches to the walls of the lesser pelvis, separating the pelvic cavity from the perineum inferiorly (region which includes the genitalia and anus). in order to allow for urination and defecation, there are a few gaps in the pelvic floor. there are two ‘holes’ that have significance. The pelvic floor is a dome shaped muscular sheet separating the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region below. this cavity encloses the pelvic viscera bladder, intestines, and uterus (in females). [1] the main function of the pelvic floor muscles are: to support the abdominal and pelvic viscera. to maintain the continence of urine and. The pelvic floor is formed by the bowl or funnel shaped pelvic diaphragm, consisting of the levator ani and coccygeus muscles and their investing fascia. structurally, the pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity from the perineum. functionally, these pelvic floor muscles support the pelvic organs, keeping them in place and preventing prolapse. The pelvic floor includes a network of muscles that supports internal organs — including parts of the male reproductive system — as well as the connecting joints, tissues and nerves. the pelvic floor muscles support organs inside the pelvis and abdomen, including the bladder, prostate, colon and rectum. a healthy pelvic floor allows for.

Posterior Pelvic Floor Muscles The pelvic floor is formed by the bowl or funnel shaped pelvic diaphragm, consisting of the levator ani and coccygeus muscles and their investing fascia. structurally, the pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity from the perineum. functionally, these pelvic floor muscles support the pelvic organs, keeping them in place and preventing prolapse. The pelvic floor includes a network of muscles that supports internal organs — including parts of the male reproductive system — as well as the connecting joints, tissues and nerves. the pelvic floor muscles support organs inside the pelvis and abdomen, including the bladder, prostate, colon and rectum. a healthy pelvic floor allows for. The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, [1] which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. [2] the pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. [3] and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the. The pelvic floor – also known as the pelvic diaphragm – is an important structure with many functions including providing support for the pelvic organs. we can see this nicely in our images. in both sexes, it provides support for the bladder and the intestines while in females, it also supports the uterus .

Pelvic Diaphragm The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, [1] which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. [2] the pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. [3] and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the. The pelvic floor – also known as the pelvic diaphragm – is an important structure with many functions including providing support for the pelvic organs. we can see this nicely in our images. in both sexes, it provides support for the bladder and the intestines while in females, it also supports the uterus .
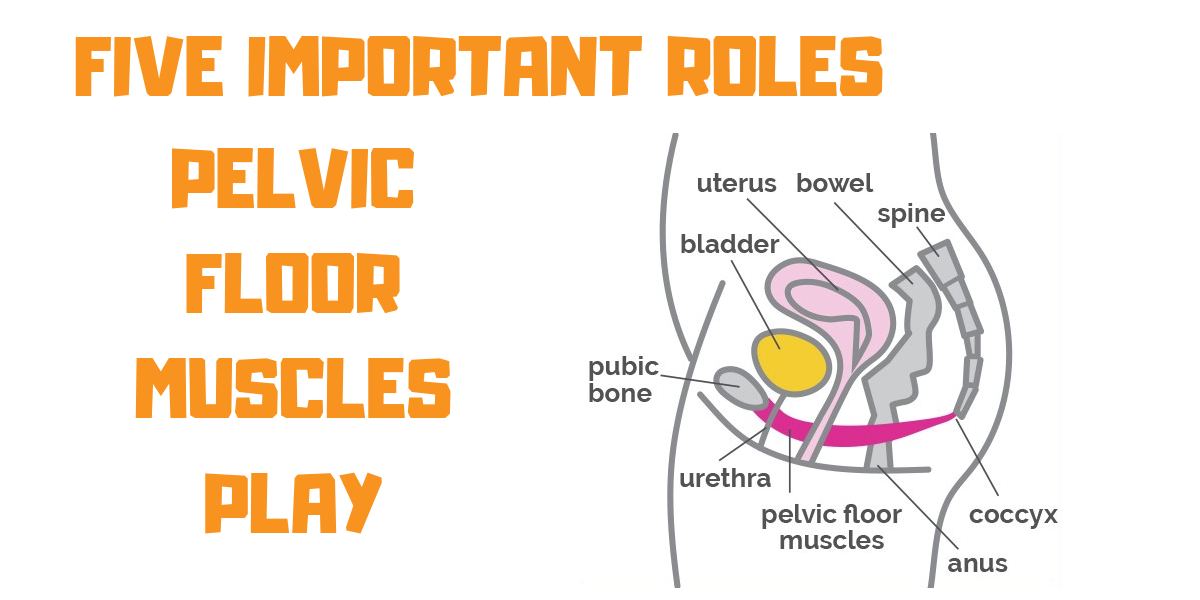
Pelvic Floor Muscles Five Important Roles Propel Physiotherapy

Comments are closed.