🥇 Oral Cavity Lips And Cheeks Anatomy Simple Explanation
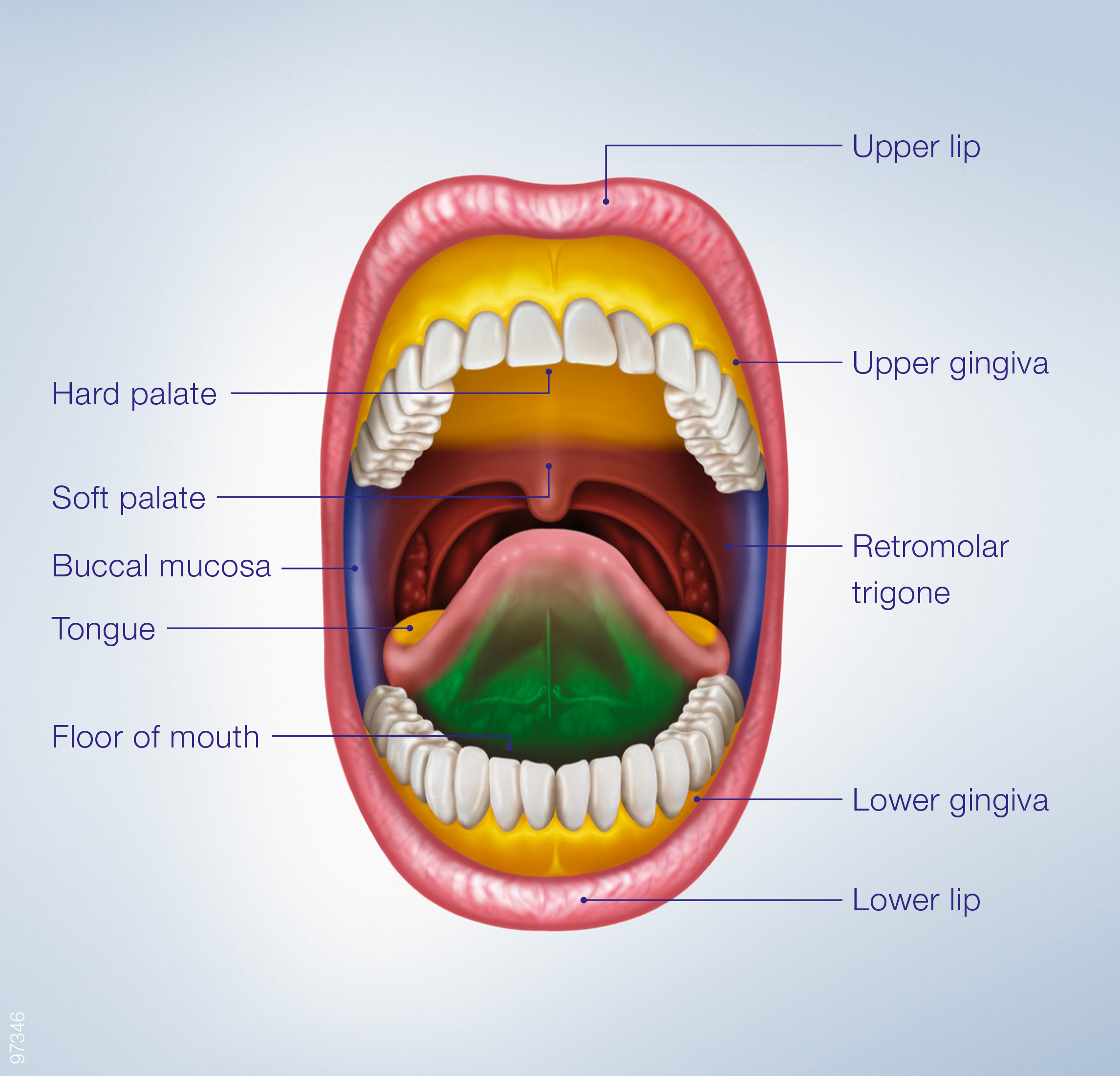
Oral Cavity Labeled Anatomy Images And Photos Finder Oral cavity. the oral cavity sits below the nose at the front of the face. it has a roof, floor, and side walls. it opens at the front as the mouth opens and connects to the throat at the back through a narrow passage called the oropharyngeal isthmus. this passage is surrounded by soft tissue. several bones make up the structure of the oral cavity:. Oral cavity. the oral cavity is situated anteriorly on the face, under the nasal cavities.it is bounded by a roof, a floor and lateral walls. anteriorly it opens to the face through the oral fissure, while posteriorly the oral cavity communicates with the oropharynx through a narrow passage called the oropharyngeal isthmus (also termed the isthmus of the fauces).

Anatomy Of The Mouth Diagram The mouth also plays a major role in the production of speech through the movements of the tongue, lips and cheeks. the mouth is a hollow cavity formed by the space between the lips, cheeks, tongue, hard and soft palates and the throat. its external opening is located along the body's midline inferior to the nose and superior to the chin. The oral cavity, better known as the mouth, is the start of the alimentary canal. it has three major functions: digestion – receives food, preparing it for digestion in the stomach and small intestine. communication – modifies the sound produced in the larynx to create a range of sounds. breathing – acts as an air inlet in addition to the. Vestibule of the mouth. the vestibule is a narrow space that lies outside the teeth and gums, and inside the lips and cheeks. it is limited above and below by the reflection of the mucus membrane from the lips and cheeks to the gums. when the mouth is open, it freely communicates with the oral cavity proper. 25.1 introduction. technically, the oral cavity consists of the vestibule between the lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and alveolar processes internally and the larger oral cavity proper located internal to the dental arches. in clinical practice, the whole mouth is simply referred to as the oral cavity, but ‘vestibule’ is used for.

Oral Cavity Anatomy Oral Cavity The Mouth Or Oral Cavity Extends Vestibule of the mouth. the vestibule is a narrow space that lies outside the teeth and gums, and inside the lips and cheeks. it is limited above and below by the reflection of the mucus membrane from the lips and cheeks to the gums. when the mouth is open, it freely communicates with the oral cavity proper. 25.1 introduction. technically, the oral cavity consists of the vestibule between the lips and cheeks externally and the teeth and alveolar processes internally and the larger oral cavity proper located internal to the dental arches. in clinical practice, the whole mouth is simply referred to as the oral cavity, but ‘vestibule’ is used for. The oral cavity, or more commonly known as the mouth or buccal cavity, serves as the first portion of the digestive system. it consists of several different anatomically different aspects that work together effectively and efficiently to perform several functions. these aspects include the lips, tongue, palate, and teeth. although a small compartment, the oral cavity is a unique and complex. The mouth. the cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). the structures of the mouth are illustrated in. at the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper.
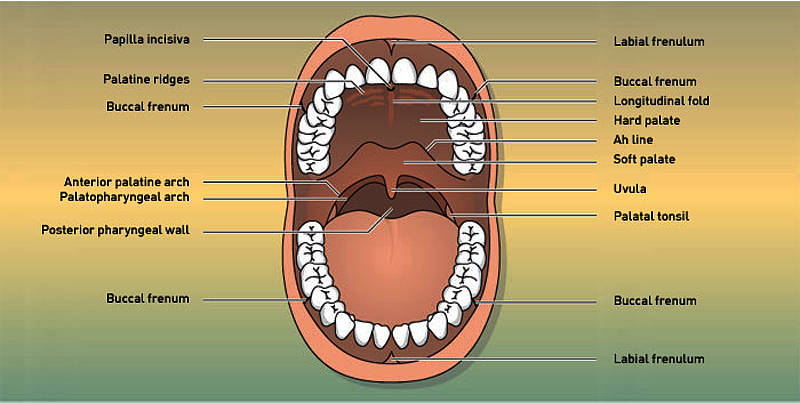
The Oral Cavity Is Limited By The Palate The Base Of The Mouth The The oral cavity, or more commonly known as the mouth or buccal cavity, serves as the first portion of the digestive system. it consists of several different anatomically different aspects that work together effectively and efficiently to perform several functions. these aspects include the lips, tongue, palate, and teeth. although a small compartment, the oral cavity is a unique and complex. The mouth. the cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). the structures of the mouth are illustrated in. at the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper.
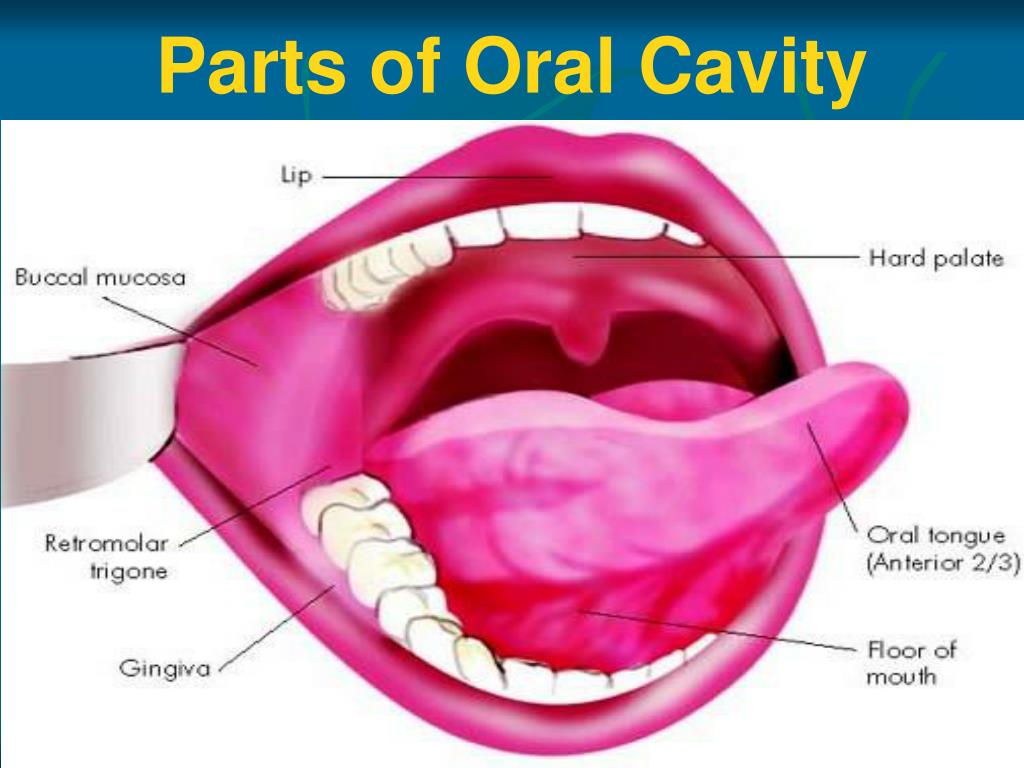
Ppt Anatomy Of Oral Cavity Pharynx Oesophagus Powerpoint

Comments are closed.