рџ Heredity And Evolution Lecture 1 Gene Chromosome And Dna Mh

рџ Heredity And Evolution Lecture 1 Gene Chromosome And Dna Mh Mendel’s 2nd law: an example. round ( r) vs wrinkled (r) seeds yellow (y) vs green (y) seeds round and yellow are dominant. step 1: cross strain producing round yellow seeds with strain producing wrinkled green seeds result: the f1 seeds are round and yellow step 2: self fertilize f1 plants result: 9 16 of plants are round and yellow 3 16 of. Chromosomes. amino acids. nucleotides. most genes contain the information to direct the synthesis of a polypeptide. the order of amino acids in the polypeptide is specified according to the code. genetic. place the molecules produced when a gene is expressed in the correct sequence beginning with the gene. mrna.
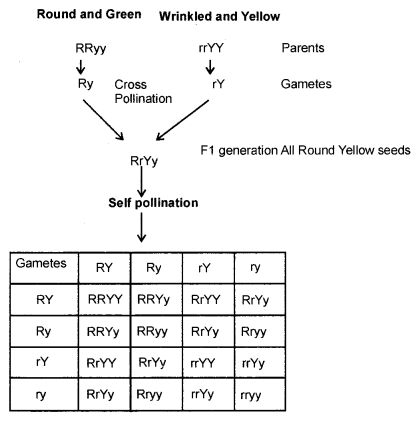
Notes Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Heredity Genetics lecture chapter 1 genes, genomes, and genetic analysis. what is a gene? click the card to flip 👆. the basic unit of biological information and heredity, made up of segments of dna on a chromosome, encodes for a particular protein or structural rna molecule. click the card to flip 👆. Chromosome, gene and dna structure explained in the easiest way.must watch. like share and subscribe.if you want a video made on any topic post it in the com cbse exam, class 10. In evolutionary biology, dna, chromosomes, and genes play integral roles in the passing of genetic information from one generation to another, ultimately driving the process of evolution. the mechanisms of inheritance, replication, and transcription are central to understanding how these components shape the genetic makeup of organisms over time. Evolutionary genetics studies the origins of and genetic relationships among organisms and the evolution of genes and genomes. genes and chromosomes genes the physical units of heredity, now known to be defined dna sequences chromosomes long molecules of double stranded dna and protein, which carry genes sexually reproducing organisms.
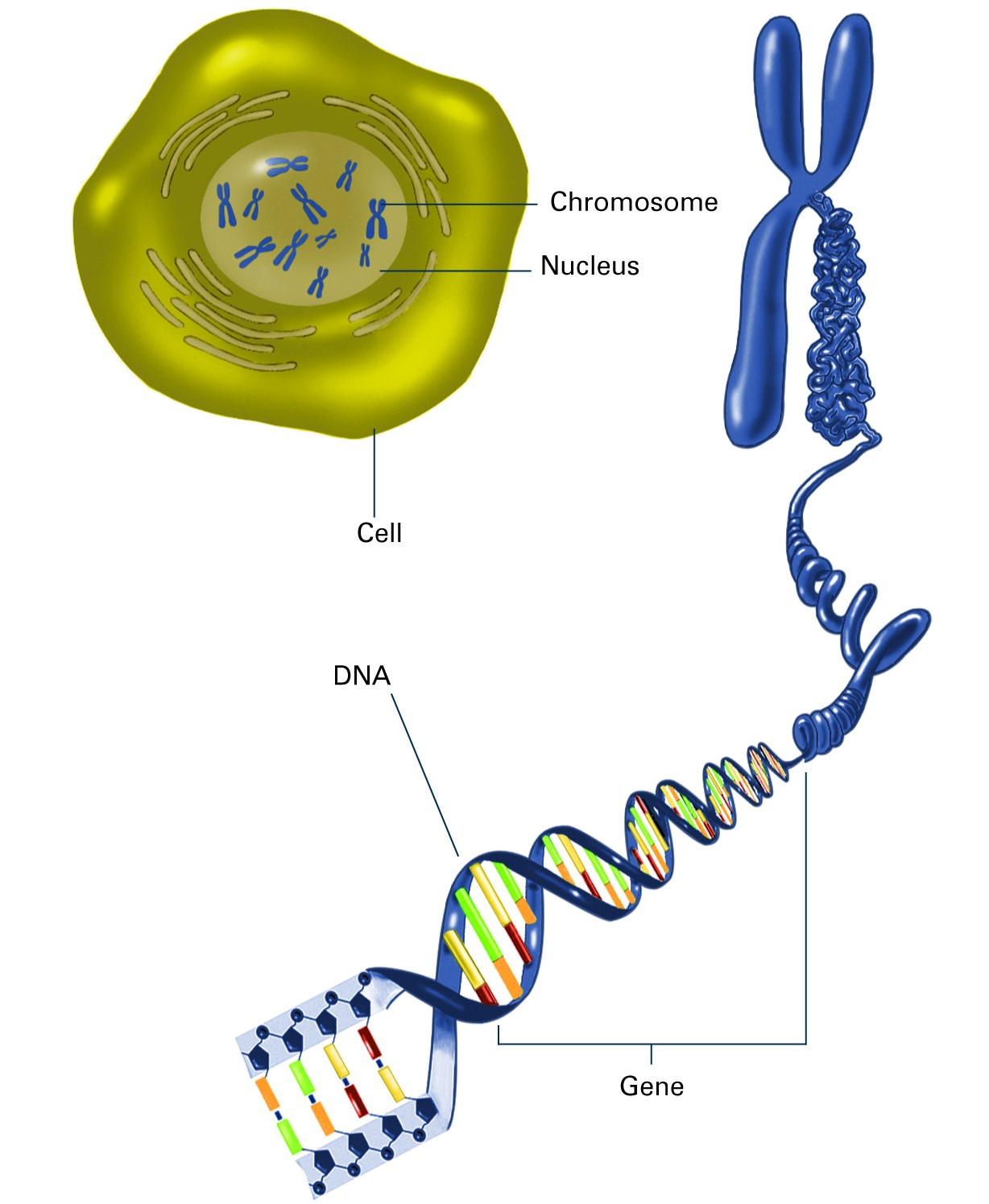
Genetics In evolutionary biology, dna, chromosomes, and genes play integral roles in the passing of genetic information from one generation to another, ultimately driving the process of evolution. the mechanisms of inheritance, replication, and transcription are central to understanding how these components shape the genetic makeup of organisms over time. Evolutionary genetics studies the origins of and genetic relationships among organisms and the evolution of genes and genomes. genes and chromosomes genes the physical units of heredity, now known to be defined dna sequences chromosomes long molecules of double stranded dna and protein, which carry genes sexually reproducing organisms. Explore dna structure function, chromosomes, genes, and traits and how this relates to heredity! video can replace old dna structure & function video and in. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) carries the information and templates for making and maintaining all living things, including people. dna contains long chains of chemicals called bases. these chains coil into 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent. rna (ribonucleic acid) is similar to dna; it also contains long chains of bases connected by a sugar.

Bbc Gcse Bitesize Genetic Information Explore dna structure function, chromosomes, genes, and traits and how this relates to heredity! video can replace old dna structure & function video and in. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) carries the information and templates for making and maintaining all living things, including people. dna contains long chains of chemicals called bases. these chains coil into 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent. rna (ribonucleic acid) is similar to dna; it also contains long chains of bases connected by a sugar.

Comments are closed.